Do fast blockchains have to sacrifice security? The blockchain trilemma
Whereas tradeoffs are unavoidable, consultants interviewed by crypto.information consider that the blockchain trilemma sheds mild on the challenges builders face and methods to navigate them.
The blockchain trilemma, coined by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin in 2017, highlights the challenges builders face in creating distributed ledger methods. In line with Buterin, architects should make tradeoffs and prioritize two out of three key options.
In an interview with crypto.information, Luke Nolan, a analysis affiliate at CoinShares, concurred with this viewpoint. Nolan believes that, in a broad sense, the blockchain trilemma successfully illustrates the problem of reaching all three options to their fullest extent. He emphasised that builders usually sacrifice some elements or each when optimizing one function.
The blockchain trilemma
Alex Dulub, Founding father of Web3 Antivirus, means that dashing up a blockchain can typically compromise its security. He believes that options like Layer-2 (L2) networks and sidechains, dealing with transactions outdoors the primary blockchain, can increase pace and scalability however could introduce new dangers.
Dulub thinks that good contract bugs, centralization dangers, and potential assaults are the important thing vulnerabilities for blockchains aiming to enhance all three elements.
Neville Grech, the founding father of Dedaub, a blockchain safety agency, factors out that growing parameters similar to block measurement and frequency to reinforce pace could demand extra computational energy, bandwidth, and storage than common nodes can deal with. This might result in a extra centralized community construction, with only some nodes absolutely taking part within the blockchain.
Whereas adjusting the validation course of would possibly pace up a community, Grech warns that “it might expose the blockchain to vulnerabilities and validation disputes and create short-term forks.”
Furthermore, in keeping with him, decreased participation of nodes and validators within the verification course of might compromise the community’s decentralization and the integrity of the blockchain.
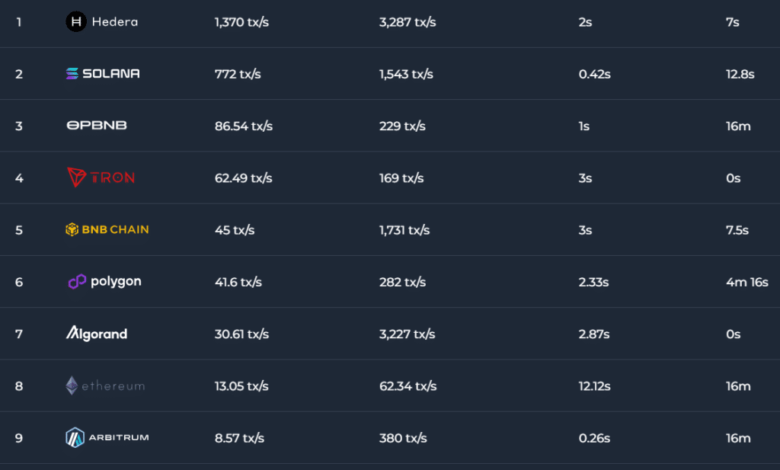
As an example, the Bitcoin community, regardless of being decentralized and safe with over a million BTC miners worldwide, processes a mean of 8.35 transactions per second (TPS). This determine is considerably decrease than centralized cash transmitters like Visa, which boasts a TPS vary of 1,500 to 2,000.
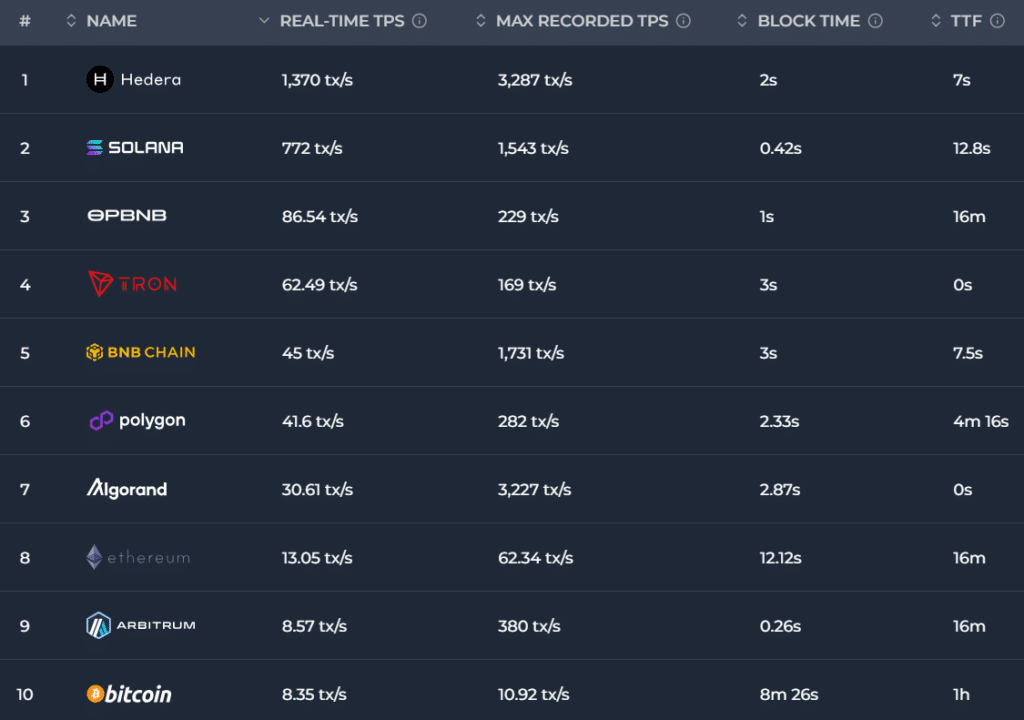
Blockchain TPS knowledge | Supply: Chainspect
In distinction, Zcash’s blockchain sometimes operates at a mean pace of 26 transactions per second (TPS) for non-shielded transactions. Nevertheless, a September 2023 report revealed that over 50% of Zcash’s hash charge was managed by the ViaBTC mining pool, exposing the community to the danger of a 51% assault.
Take Solana (SOL) as one other instance, boasting a present real-time TPS of 772, in keeping with Chainspect knowledge. Regardless of dealing with its tenth main outage in February 2023, the community has demonstrated excessive stability since then.
In a July 21, 2023 report, the Solana Basis declared a 100% uptime for the Solana blockchain. This achievement adopted enhancements within the ratio of voting-to-non-voting transactions.
On this case, Luke Nolan, a analysis affiliate at CoinShares, factors out that the first tradeoff made was with decentralization, and in keeping with him, “safety has come at a extra minimal tradeoff.”
He highlights that the value of operating a Solana validator might be fairly excessive, ranging between $3,000 and $5,000. This excessive value makes it costly for most of the people to function a Solana validator, posing dangers of centralization.

{Hardware} necessities to run a Solana node | Supply: Solana Labs
In line with Solana Compass knowledge, Solana presently has a complete of two,919 nodes with greater than 433,000 stakers. The variety of the community’s nodes has declined considerably since March 2023 after reaching an all-time excessive (ATH) of two,564 working nodes.
Whereas the variety of Ethereum nodes has been constantly declining since mid-January, presently hovering round 7,000, it’s nonetheless 2.4 instances increased than Solana’s working gadgets.
You may also like: Pace vs decentralization: might L2 options undermine cryptocurrency core ethos?
This quantity is cheap on condition that Ethereum nodes require decrease {hardware} necessities in comparison with Solana and value between $500 and $1,000. As well as, the variety of Ethereum stakers can be considerably increased than Solana’s — presently standing at over 921,000.
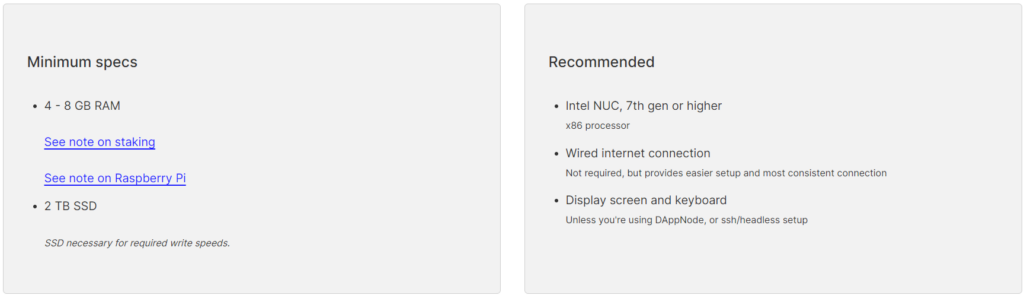
{Hardware} necessities to run an Ethereum node | Supply: Ethereum.org
Nolan additionally talked about that Ethereum has, for now, put apart the concept of Layer-1 (L1) scaling to keep away from compromising decentralization or safety. Presently, Ethereum handles a mean of round 13 transactions per second (TPS), with its highest recorded TPS reaching 62.34.
“General, I wouldn’t say the variety of validators is the #1 metric of decentralization, however from a philosophical perspective, you could possibly run an Ethereum node for very low-cost, assist progress the chain even with out staking 32 ETH — though in fact, you wouldn’t earn something.”
Luke Nolan instructed crypto.information.
Options
To indicate that the blockchain trilemma isn’t an unbreakable rule, firms are introducing artistic options that problem the concept that pace and safety are all the time at odds. Let’s discover a number of the prime options that intention to steadiness scalability, safety, and decentralization.
- L2 networks: These options improve Layer-1 blockchains by boosting transaction pace, reducing charges, and enhancing total scalability. L2s let the primary chain concentrate on safety and decentralization, whereas Layer-2 networks deal with scalability and effectivity. Technically, L2 blockchains inherit the safety of L1 networks.
- Consensus mechanism adjustments: New consensus mechanisms, similar to Proof of Stake (PoS) variants, intention to steadiness safety and pace with out main compromises. Transitioning from Proof of Work (PoW) to PoS may very well be a major method to enhance transaction throughput whereas decreasing processing charges.
- Segregated Witness (SegWit): Applied in Bitcoin in 2017, SegWit scales blockchain throughput by separating transaction signatures from transaction knowledge and storing them in another way. This separation improves house effectivity, streamlines verification, and reduces the general measurement of transaction information.
- Sharding: Methods like sharding distribute transaction processing throughout smaller teams of nodes, growing pace whereas sustaining safety. Concord blockchain, for instance, makes use of sharding and presently achieves a two-second finality time, whereas Solana’s Time to Finality (TTF) is round 12.8 seconds.
-
Rollups:
- Zero-knowledge rollups (zk-rollups): These rollups bundle tons of of transactions off-chain and generate a cryptographic proof, often known as a zero-knowledge proof.
- Optimistic rollups: These function on the idea that transactions are legitimate by default. They perform the computation on the Layer-1 (L1) blockchain solely in case of a dispute. This introduces a finality delay in verifying the legitimacy of transactions earlier than they attain the L1 community. If a transaction is discovered to be invalid, it may be rolled again to stop any unfavourable penalties.
Conclusion
Quick blockchains don’t straight sacrifice decentralization and safety; as an alternative, the blockchain trilemma sheds mild on challenges builders confront and the occasional tradeoffs they have to navigate.
“In a nutshell, whereas pace usually poses tradeoff challenges with safety, the blockchain neighborhood’s relentless innovation can present some options. It’s not nearly selecting between pace and safety; it’s about neatly engineering the blockchain to steadiness each.”
Neville Grech instructed crypto.information.
Dulub emphasizes that “cautious design, rigorous testing, and ongoing analysis are key to managing the challenges” related to the blockchain trilemma.
Learn extra: Electrical energy demand to double in 3 years. How AI and mining play a component






