What Is Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS): How It Works and Why We Need It
Blockchains don’t want middlemen, however they do want consensus. That’s the place delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) is available in—it’s a blockchain consensus mechanism that makes use of neighborhood elections to maintain issues quick, environment friendly, and safe.
What Is Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)?
Delegated proof-of-stake is a consensus mechanism utilized in many blockchain networks. It helps a decentralized community agree on which transactions are legitimate and which blocks so as to add subsequent.
On this consensus protocol, token holders delegate voting energy to elect validators—additionally referred to as block producers, witnesses, or tremendous representatives. As a result of fewer individuals deal with validation, the community can attain choices sooner and at a decrease value. This method was designed to make block manufacturing faster and cheaper.
DPoS vs. Proof-of-Stake: What’s Completely different
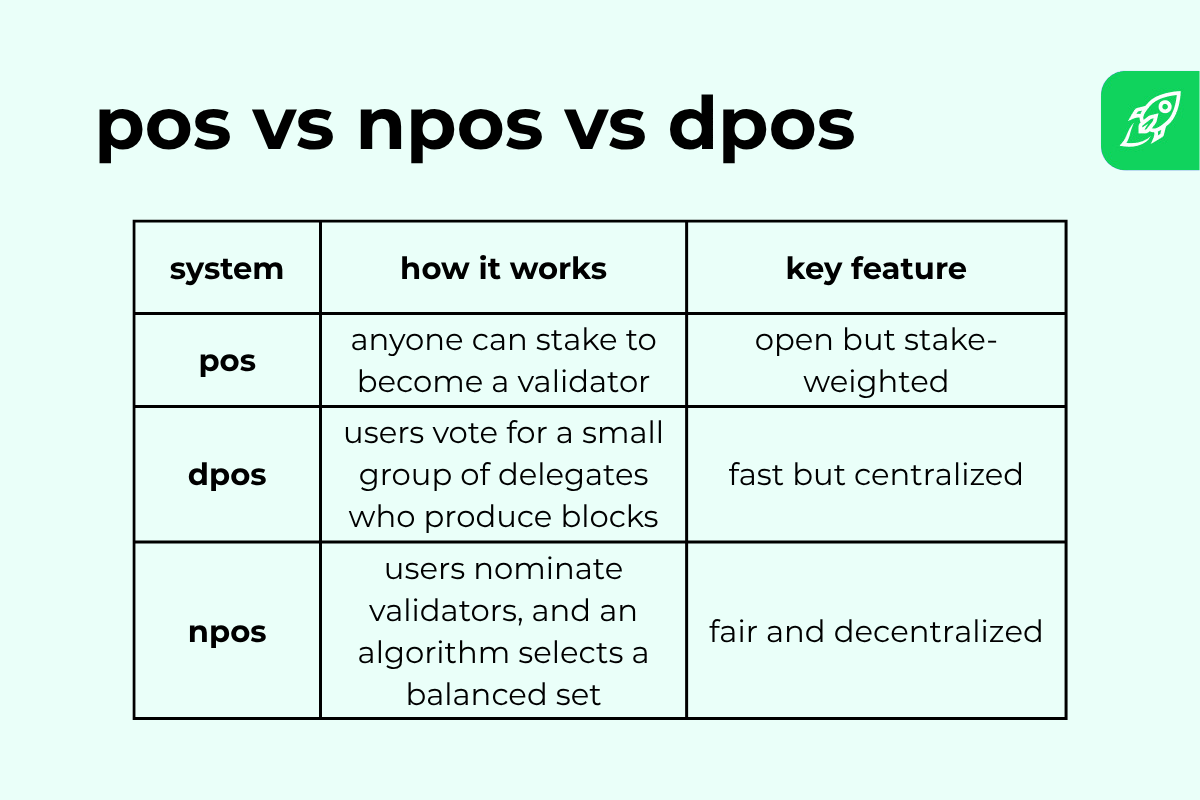
Each methods share the identical PoS idea—you stake cash to assist safe the community. However how they decide validators may be very completely different.
In a typical proof-of-stake mannequin, anybody can change into a validator by locking tokens. This PoS mechanism is permissionless, and choice is weighted by stake. Extra cash means extra probabilities to validate blocks.
Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) takes one other path. You vote for a small, elected committee to do the work. Governance in DPoS is steady, since token holders can reassign votes at any time.
This design hurries up block manufacturing however limits the variety of contributors.
Origin of Delegated Proof-of-Stake
The DPoS system was created in 2014 by software program engineer Daniel Larimer. He designed it as a sooner and fairer strategy to safe blockchains with out the heavy prices of mining. On the time, early blockchain initiatives like BitShares and Steem wanted a scalable resolution. Their communities needed excessive throughput and real-time voting.
DPoS launched a brand new consensus algorithm the place customers might elect a couple of trusted validators as an alternative of hundreds of random ones. It rapidly grew to become a preferred evolution of proof-of-stake, powering later networks resembling EOS and TRON.
How Delegated Proof-of-Stake Works (Step by Step)
The DPoS mannequin runs on a voting and delegation mechanism. It provides each person a say in who maintains the community. On this voting system, you employ your cash to elect delegates—trusted validators who affirm transactions and create blocks.
Voters keep management as a result of they will reassign their votes anytime. The system makes use of weighted voting, that means your voting weight equals your token stability. Some chains additionally set a quorum & threshold to verify solely high candidates are chosen.
Each election cycle updates who will get to validate the community subsequent.
Step 1: Token Holders Delegate Their Stake
Token holders lock part of their stake to vote. Every voter’s stake represents belief within the community. The bigger the person’s stake, the stronger their affect in elections.
Step 2: Election of Validators (Block Producers or Witnesses)
After voting, the highest block producers—typically referred to as witnesses—change into energetic validators. The delegates chosen kind a small staff accountable for operating the blockchain. Every specific delegate has equal authority to a validator, and the committee measurement is fastened, resembling 21 for EOS or 27 for TRON.
Step 3: Validator Schedule and Block Manufacturing
Energetic validators comply with a hard and fast order for block manufacturing. They take turns in a deterministic schedule, the place every proposes precisely one block per spherical. This predictable scheduling prevents overlap. Every block proposal should comply with the principles for block creation, conserving the chain safe and steady.
Step 4: How Finality Is Reached in DPoS
Validators validate transactions and confirm transactions in sequence. As soon as sufficient blocks are created and most validators validate blocks, the outcomes attain finality. Many DPoS methods use Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)—a rule that finalizes a block when two-thirds agree. Some additionally add a randomness beacon to forestall collusion or predictable validator order.
Step 5: Reward Distribution to Validators and Delegators
When validators produce a block, they earn transaction charges and typically extra tokens as rewards. These are shared by reward distribution with voters. Customers vote to help trustworthy validators and earn a part of the reward from such transactions.
Step 6: Lock-Up and Unbonding Interval Defined
Most DPoS chains require collateral staking to safe votes. The bigger the deposit, the upper your voting energy, however even a smaller stake can take part. To keep up stability, rewards are launched after an epoch, and withdrawals might take an unbonding interval. This lock-up interval ensures validators can’t abandon the community mid-cycle.
DPoS Actors and Roles
Each DPoS community depends on three primary teams: token holders, validators, and governance delegates. Collectively, these community customers preserve the system safe and truthful.
Customers resolve who validates transactions and suggest updates to enhance the community’s design. These choices form the system’s efficient operation. When everybody participates, the blockchain runs easily and stays decentralized.
Token Holders: Voters within the Community
Every voter’s stake represents a voice within the system. You possibly can help anybody you belief, and voters keep management as a result of votes may be modified anytime. This ongoing alternative retains validators accountable to their communities.
Validators: Block Producers and Community Operators
Validators maintain block validation rights. They run the software program, confirm transactions, and add new blocks. In the event that they show dangerous habits, resembling downtime or manipulation, they danger dropping help or future rewards.
Proxy Voting and Governance Delegates
DPoS chains typically help proxy voting, the place you delegate your vote to somebody extra energetic. These buildings create fascinating governance fashions that make decision-making extra financially inclusive. In addition they carry extra decentralization, since even customers with small balances can affect the community by trusted representatives.
Advantages of Delegated Proof-of-Stake
The DPoS consensus mannequin provides pace, vitality financial savings, and neighborhood management. By decreasing the variety of validators, it retains the decentralized community quick whereas nonetheless safe. That stability permits efficient operation even below heavy load.
DPoS methods energy an enormous range of blockchains, from gaming to DeFi. Every adapts the identical thought—neighborhood voting and elected validators—to its personal wants. Let’s break down what makes this mannequin so environment friendly.
Quicker Transactions and Larger Throughput
In DPoS, the validator accountable for the subsequent block is pre-determined (scheduled upfront).
So as an alternative of validators competing—like in proof-of-work—every one is aware of precisely when it’s their flip to create a block. This organized schedule removes delays and wasted effort. In consequence, the community can course of hundreds of transactions per second, reaching a lot larger throughput than older consensus methods.
Decrease Latency and Fast Finality
With fewer producers, blocks are added in fast sequence. Every new block seems inside seconds, decreasing latency and enhancing person expertise. Excessive liveness ensures the community retains operating easily, even when one validator goes offline.
Vitality Effectivity and Scalability
DPoS doesn’t depend upon mining or costly {hardware}. The computing energy required is minimal as a result of validators take turns as an alternative of racing to resolve puzzles. This protects large computing energy and makes scaling simpler because the person base grows.
On-Chain Governance and Accountability
DPoS makes use of a built-in voting system the place customers select who represents them. Effectively-informed delegators can change inactive or dishonest validators at any time, creating direct accountability contained in the protocol.
Dangers and Disadvantages of DPoS
DPoS brings pace and effectivity, however these advantages include trade-offs.
Centralization and Cartelization Threat
Having only some validators will increase cartelization danger. The identical teams might dominate elections for lengthy durations, forming alliances or buying and selling votes. This limits competitors and makes the system much less open than it seems.
Malicious Makes an attempt and Takeover Eventualities
A smaller validator set additionally makes DPoS extra weak to malicious makes an attempt to take over. If a number of validators act collectively, they might management governance or censor transactions. These takeover eventualities are more durable to attain in large-scale PoS networks with hundreds of unbiased nodes.
Double Spending and Safety Gaps
One other attainable challenge is double spending. When a couple of validators cooperate dishonestly, they could affirm conflicting transactions. This weakens safety and confuses the ledger. To cut back such assaults, most DPoS chains depend on brief election cycles and penalties for dishonest.
Lowered Censorship Resistance
Fewer validators can decrease censorship resistance. A small group might freeze accounts or delay transactions with out broad consensus. The Nakamoto coefficient—a measure of what number of entities management the community—is normally decrease in DPoS methods than in bigger proof-of-stake networks.
DPoS In comparison with Different Consensus Mechanisms
Delegated proof-of-stake is considered one of a number of consensus algorithms that assist blockchains attain settlement on legitimate transactions. Each consensus protocol has trade-offs between pace, safety, and decentralization. Understanding these variations helps you see the place DPoS matches into fashionable blockchain expertise.
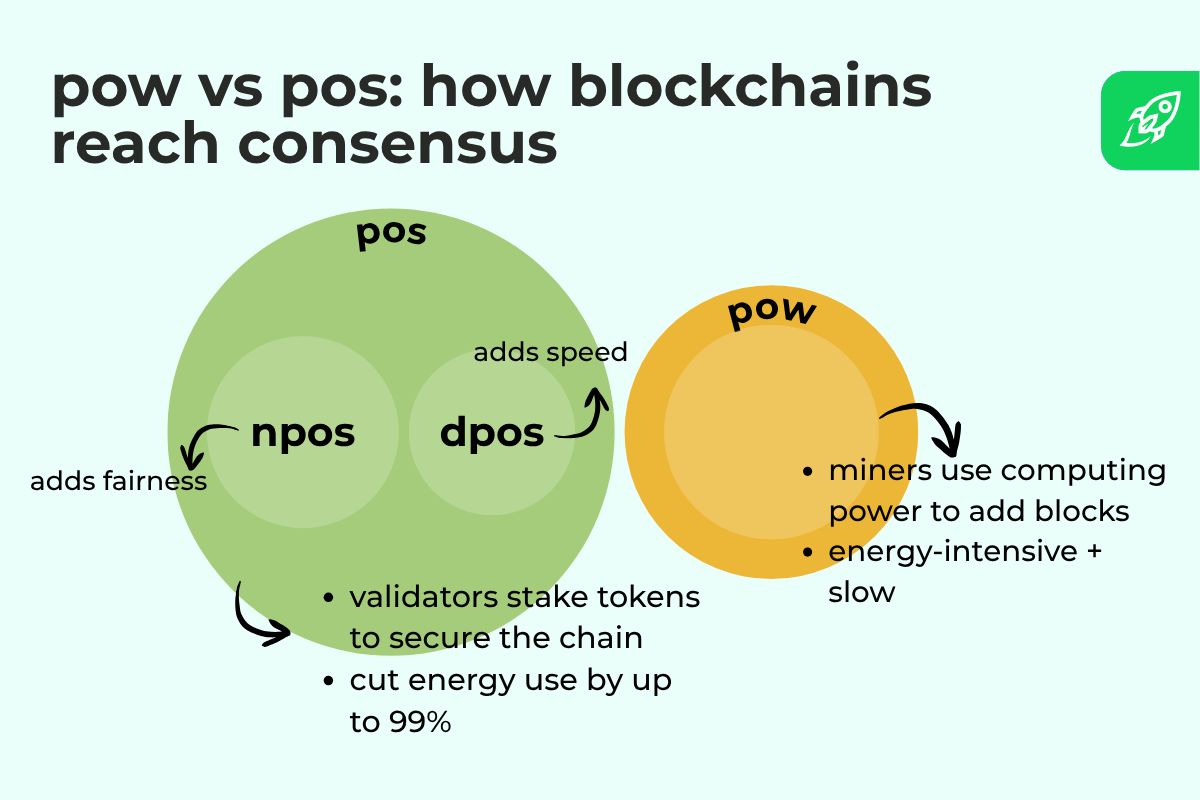
DPoS vs. Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Proof-of-work was the primary consensus mannequin, utilized by Bitcoin. It depends on miners fixing advanced puzzles with large computing energy. This design makes assaults costly but additionally slows down block creation and wastes vitality.
In DPoS, there’s no competitors to search out new blocks. As a substitute, a couple of trusted validators take turns confirming transactions. This offers DPoS sooner block occasions and decrease vitality use however reduces openness—solely elected validators have block validation rights.
Whereas PoW secures blockchains by value and electrical energy, DPoS achieves effectivity by coordination and neighborhood voting.
DPoS vs. Nominated Proof-of-Stake (Polkadot)
Polkadot makes use of nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS), a system designed to keep up equity and scalability. On this mannequin, nominators help validators by contributing to a staking pool. The community then chooses a various validator set to maximise safety.
Polkadot (NPoS) robotically rotates validators, decreasing focus of energy. In comparison with DPoS, NPoS is much less depending on public elections and extra targeted on random choice and slashing guidelines to forestall misconduct.
Learn additionally: What Is Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS)?
DPoS vs. Liquid Proof-of-Stake (Tezos)
Tezos (Liquid PoS) works like a versatile model of PoS. Customers can delegate their tokens to “bakers” however don’t lose management of them. This retains funds liquid and permits extra decentralization, since small holders can nonetheless take part with out locking their tokens.
DPoS, against this, makes use of direct elections and stuck validator counts. It’s sooner however much less open. Tezos favors inclusivity, whereas DPoS prioritizes efficiency and easy governance.
Actual-World Examples of DPoS Blockchains
Many DPoS blockchains present how delegation and voting work in actual life. Every one adapts the identical mannequin to completely different blockchain functions—from funds to content material platforms. Let’s have a look at among the best-known blockchain initiatives utilizing DPoS right now.
EOS and Its Block Producers
EOS is without doubt one of the largest Delegated Proof networks. It depends on 21 block producers, elected by token holders. Every producer indicators blocks in a hard and fast schedule, creating a block each 0.5 seconds.
Blocks attain finality when 15 of 21 producers affirm them, giving the community quick and safe efficiency. EOS exhibits how a small validator set can keep stability by frequent elections and clear reward guidelines.
TRON and Its Tremendous Representatives
TRON makes use of 27 validators, referred to as Super Representatives, who’re re-elected each six hours. Every one produces blocks for a brief slot earlier than passing it on.
The community averages a three-second block time and rewards every validator with TRX tokens per block produced. This setup exhibits DPoS as a sensible mannequin for a high-speed, low-cost funds community.
Steem and Its Witness Governance
Steem makes use of 21 validators, referred to as witnesses, to supply blocks. These witnesses are re-elected typically, conserving the system energetic and accountable.
If a witness fails to supply blocks, voters can change them immediately. This rotation retains Steem responsive and demonstrates how on-chain democracy works in actual time.
BitShares: Early Use of DPoS
BitShares was the primary venture to make use of DPoS efficiently. It launched approval voting to pick high validators and impressed later networks like EOS and Steem.
This early experiment proved that decentralization might nonetheless thrive with out energy-heavy mining, paving the best way for environment friendly governance and sooner validation.
Sui and Trendy DPoS Variations
Sui (DPoS-style) makes use of delegated staking with a whole lot of validators. Every epoch lasts about 24 hours, and validators finalize transactions utilizing fashionable consensus layers like Narwhal and Bullshark.
Sui blends conventional DPoS design with cutting-edge tech to enhance scalability. It’s one of the vital financially inclusive and fascinating governance fashions amongst fashionable smart-contract platforms, exhibiting how versatile delegation can energy next-generation methods.
Remaining Ideas
Delegated proof-of-stake exhibits how democracy can energy pace. By letting customers vote for trusted validators, it creates environment friendly but clear methods. Regardless of some centralization dangers, DPoS provides sturdy community safety and good safety in opposition to failures. Its evolution proves that governance and efficiency can coexist in fashionable blockchain design.
Disclaimer: Please be aware that the contents of this text are usually not monetary or investing recommendation. The knowledge supplied on this article is the creator’s opinion solely and shouldn’t be thought of as providing buying and selling or investing suggestions. We don’t make any warranties in regards to the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this data. The cryptocurrency market suffers from excessive volatility and occasional arbitrary actions. Any investor, dealer, or common crypto customers ought to analysis a number of viewpoints and be acquainted with all native rules earlier than committing to an funding.






