What are open-source protocols, and how do they work?
Understanding open-source protocols
Open-source protocols have turn into a mainstay within the tech world and are gaining traction because of the myriad advantages that they provide over their proprietary counterparts.
The protocols are usually created with the intention of being utilized by the general public, enabling anybody to look at, alter and share their code. The advantages of open-source protocols are multifaceted, starting from their inherent transparency to their wider accessibility.
Moreover, they depend on peer evaluations, a cheap and inclusive mannequin that distinguishes them from their proprietary counterparts. Distinguished examples of open-source software program embody extensively used working programs similar to Linux and Android and the favored Firefox net browser.
In the case of open-source cryptographic protocols, the Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano and Polkadot networks stand out as noteworthy blockchain protocol exemplars, amongst others.
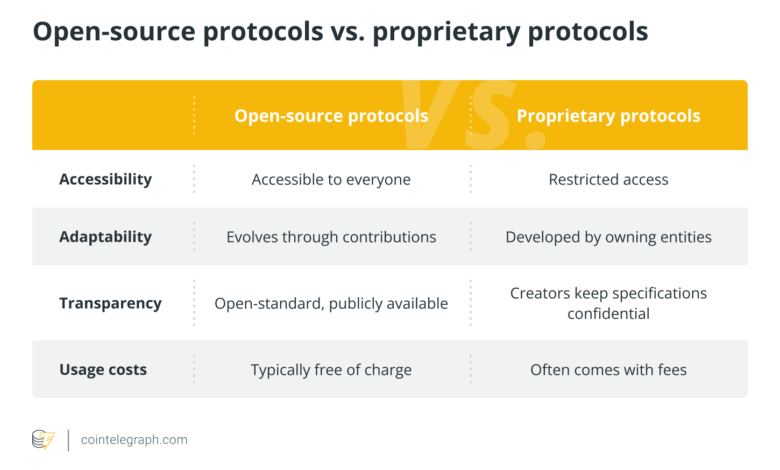
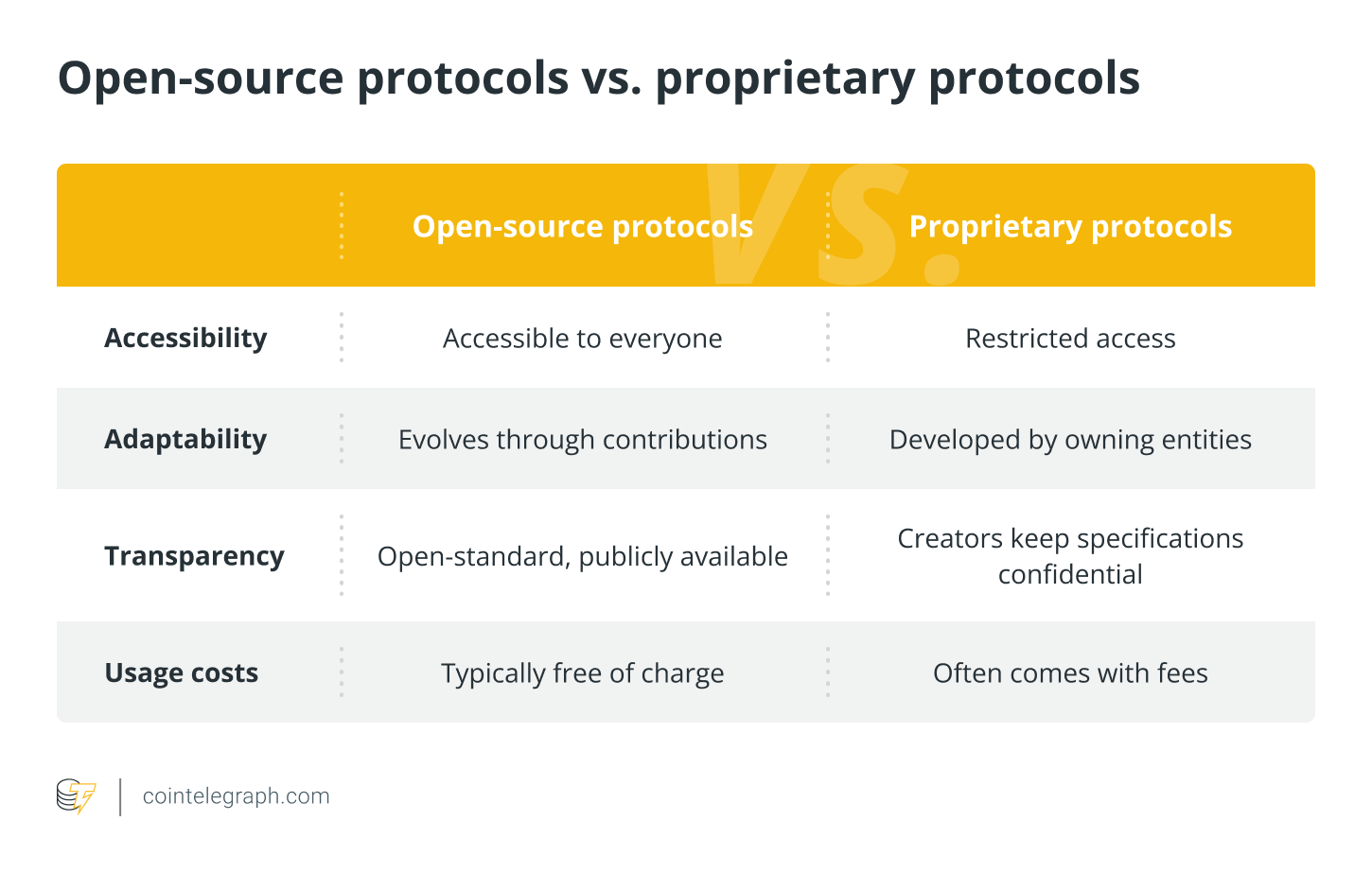
Open-source vs. proprietary protocols
Open-source and proprietary protocols signify two distinct approaches to protocol growth, every with its personal set of rules in the case of protocol implementation.
The next is a dissection of their key disparities:
What’s the event course of for open-source protocols?
The event of open-source protocols includes a number of distinct phases, every integral to a protocol’s evolution. All of it begins with the conceptualization part, the place builders lay the inspiration that defines the protocol’s requirements and objective.
Normally, the essential idea is predicated on an current protocol with some enhancements. The conceptualization stage acts because the bedrock, upon which builders meticulously define the structure and options, forming a strong theoretical basis. On this part, builders chart out a well-defined roadmap, akin to a strategic plan, guiding the mission’s trajectory.
The next step within the growth course of is often the prototyping stage. On this stage, builders create a useful mannequin of the protocol that features the important thing proposed options. The prototype is often made accessible to the general public because the beta model.
Releasing the beta model topics the software program to real-world eventualities and consumer interactions, permitting builders to discern its strengths and weaknesses. The stage additionally permits builders to get suggestions from the open-source neighborhood relating to potential new options to include earlier than the ultimate protocol is launched. Subsequently, the stage is aptly known as the beta testing or consumer acceptance testing (UAT) stage.
Steady suggestions and updating make sure that the protocol stays attentive to the evolving wants and expectations of its consumer base. After related protocol upgrades are applied to resolve lots of the identified stability and reliability points, the protocol reaches a degree of stability warranting the designation of a “steady launch.” The steady launch model is often as dependable as builders could make it.
Nonetheless, the method doesn’t culminate in steady releases. Open-source tasks require ongoing protocol upkeep. The method often entails releasing bug fixes, similar to safety patches, and updating the code for enhanced compatibility.
Are open-source protocols copyrighted?
When a developer publishes their code as open-source, they’re sharing it with the general public, permitting others to make use of, modify and distribute it. Nonetheless, the act of constructing the code public doesn’t translate to unrestricted utilization.
Copyright legal guidelines apply right here, simply as they do for proprietary software program. The legal guidelines routinely safeguard any authentic artistic work, together with open-source protocols, granting the software program creator unique rights to regulate their use and distribution.
In the case of open-source protocol licensing, the developer usually attaches a license to it, which acts as a set of pointers that clearly delineates what’s permissible and what’s off-limits regarding the code.
Open-source licenses usually grant customers in depth permissions without having express approval from the unique writer. That mentioned, there are two principal sorts of open-source licenses: permissive and copyleft.
A permissive license, generally additionally known as a BSD-style or Apache-style license, imposes minimal necessities on how the software program could be modified or redistributed. Nonetheless, tasks that use any such license are obliged to append a guaranty disclaimer. A basic instance of a permissive license is the MIT License. The license permits anybody to make use of, modify and distribute the code with out prior consent.
Tasks using MIT-licensed code usually should incorporate the unique copyright discover and a disclaimer explicitly stating that the software program comes with none guarantee. The disclaimer clarifies that the copyright holders bear no duty for any claims or liabilities stemming from the software program’s use.
The license is exceedingly permissive and is crafted to supply most freedom to builders, even allowing the code’s inclusion and distribution in business merchandise.
Relating to copyleft licenses, tasks that use them are additionally required to affix a legal responsibility disclaimer. They arrive with extra restrictions, particularly regarding the distribution of modified protocol variations. For example, the copyleft GNU Basic Public License (GPL), a extensively employed open-source license, ensures that the software program stays open and free. Just like the MIT License, the GPL mandates a guaranty disclaimer.
Copyleft licenses assure that open-source protocols or software program could be utilized, tweaked and shared with out constraints. Nonetheless, any modified work should adhere to the identical phrases, preserving the protocol’s openness in all future variations.
In the case of proprietary protocols, the panorama modifications dramatically. The protocols impose stringent limitations on their protocol documentation, which frequently embody restrictions on modifying or reverse-engineering the code.
To uphold protocol safety, proprietary tasks often embody confidentiality clauses of their licenses, stopping customers from disclosing their protocols’ workings or any proprietary info they could come throughout.
When it comes to price, permissive and copyleft licenses are free, permitting customers to make use of and distribute the software program with out cost. In distinction, proprietary licenses usually require customers to pay for entry to and use of the software program.
The way forward for open-source protocols
Because the world turns into more and more digital and interconnected, open-source protocols are poised to play a key function in enabling innovation, particularly in the case of supporting interoperability amongst totally different programs, functions and gadgets.
The shift is pushed by the widespread, concurrent utilization of protocols crafted by totally different builders on an on a regular basis foundation. Consequently, open-source protocols, particularly those who enable alterations by third events and help interoperable programs, are certain to take middle stage within the new technological frontier.
Going by present traits, open-source tasks are additionally prone to concentrate on sustainability, vitality effectivity and problem-solving in alignment with the worldwide push for eco-friendly technological options.
Moreover, open-source networking protocol initiatives are anticipated to proceed creating peer-to-peer (P2P) web protocols. The protocols facilitate direct communication between programs, eliminating the necessity for centralized middleman programs. P2P protocols boast an increasing array of functions, significantly in enabling P2P transactions and communications by decentralized protocols.






